
It can use preshared keys, RSA signatures, or GSS-API. The racoon IKEv1 key management daemon negotiates and configures a set of parameters for IPSec.
#Could not get mac address for nic: software loopback interface 1 udeploy agent manual
If manual key encryption with IPsec is being used, refer to /usr/share/doc/initscripts- /sysconfig.txt (replace with the version of the initscripts package installed) for configuration parameters. Both applications are part of the ipsec-tools package. This is only used for network-to-network IPsec configurations. Where is the network address of the IPsec source network. This setting is optional and is only used for host-to-host IPsec configurations. Where is the IP address of the IPsec source host or router. Where is the network address of the IPsec destination network. This is used for both host-to-host and network-to-network IPsec configurations. Where is the IP address of the IPsec destination host or router. This directive is deprecated, as the value is

Refer to Section 13.2.3, “Channel Bonding Interfaces” for more information about channel bonding interfaces. This directive is used in conjunction with the SLAVE directive.
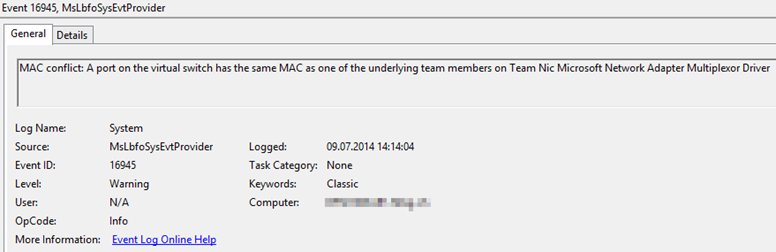
Where is the channel bonding interface to which the This directive should not be used in conjunction with This directive is used to assign a MAC address to an interface, overriding the one assigned to the physical NIC. Should not be used in conjunction with MACADDR.ĪA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF. This directive is useful for machines with multiple NICs to ensure that the interfaces are assigned the correct device names regardless of the configured load order for each NIC's module. Where is the hardware address of the Ethernet device in the formĪA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF.

Where is the IP address of the network router or gateway device (if any). This needs to be stated first, as the option entries are order-dependent. However, it is also possible to manually edit the configuration files for a given network interface.īelow is a listing of the configurable parameters in an Ethernet interface configuration file:Ĭhanging speed or duplex settings almost always requires disabling autonegotiation with the autoneg off option. The Network Administration Tool ( system-config-network) is an easy way to make changes to the various network interface configuration files (refer to Chapter 14, Network Configuration for detailed instructions on using this tool). For example, the ifcfg-eth0 file for an interface using DHCP looks different because IP information is provided by the DHCP server: The values required in an interface configuration file can change based on other values. The following is a sample ifcfg-eth0 file for a system using a fixed IP address: Because each device has its ownĬonfiguration file, an administrator can control how each interface functions individually. There are multiple ifcfg-eth files (where is a unique number corresponding to a specific interface). One of the most common interface files is ifcfg-eth0, which controls the first Ethernet network interface card or NIC in the system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
